Table Of Content
Greenhouse gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and water vapor significantly affect the amount of energy in the Earth system, even though they make up a tiny percentage of Earth’s atmosphere. Solar radiation that passes through the atmosphere and reaches Earth’s surface is either reflected or absorbed. Reflected sunlight doesn’t add any heat to the Earth system because this energy bounces back into space. Some scientists have suggested that we could terraform the surface of Mars by sending "factories" that would spew water vapor, carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the air.
More Greenhouse Gases = A Warmer Earth
Releasing greenhouse gases intensifies the greenhouse effect, and increases Earth’s average air temperatures (also known as global warming). Hover over or click on the icons to learn more about these human causes of change and how they influence the greenhouse effect. Over the last century, burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2).
Eunice Newton Foote: The woman who discovered the greenhouse effect - New Scientist
Eunice Newton Foote: The woman who discovered the greenhouse effect.
Posted: Mon, 17 Jul 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
MethaneSAT
NASA explores the unknown in air and space, innovates for the benefit of humanity, and inspires the world through discovery. "I’ve concluded that repairing our relationship across the political divide can only be done with someone else at the helm,'' Yousaf told reporters in Edinburgh, Scotland's capital. To learn more about what is the greenhouse effect, its definition, causes and effects, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download the BYJU’S app for further reference. Nitrous oxide used in fertilizers is one of the contributors to the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere.
The Greenhouse Effect
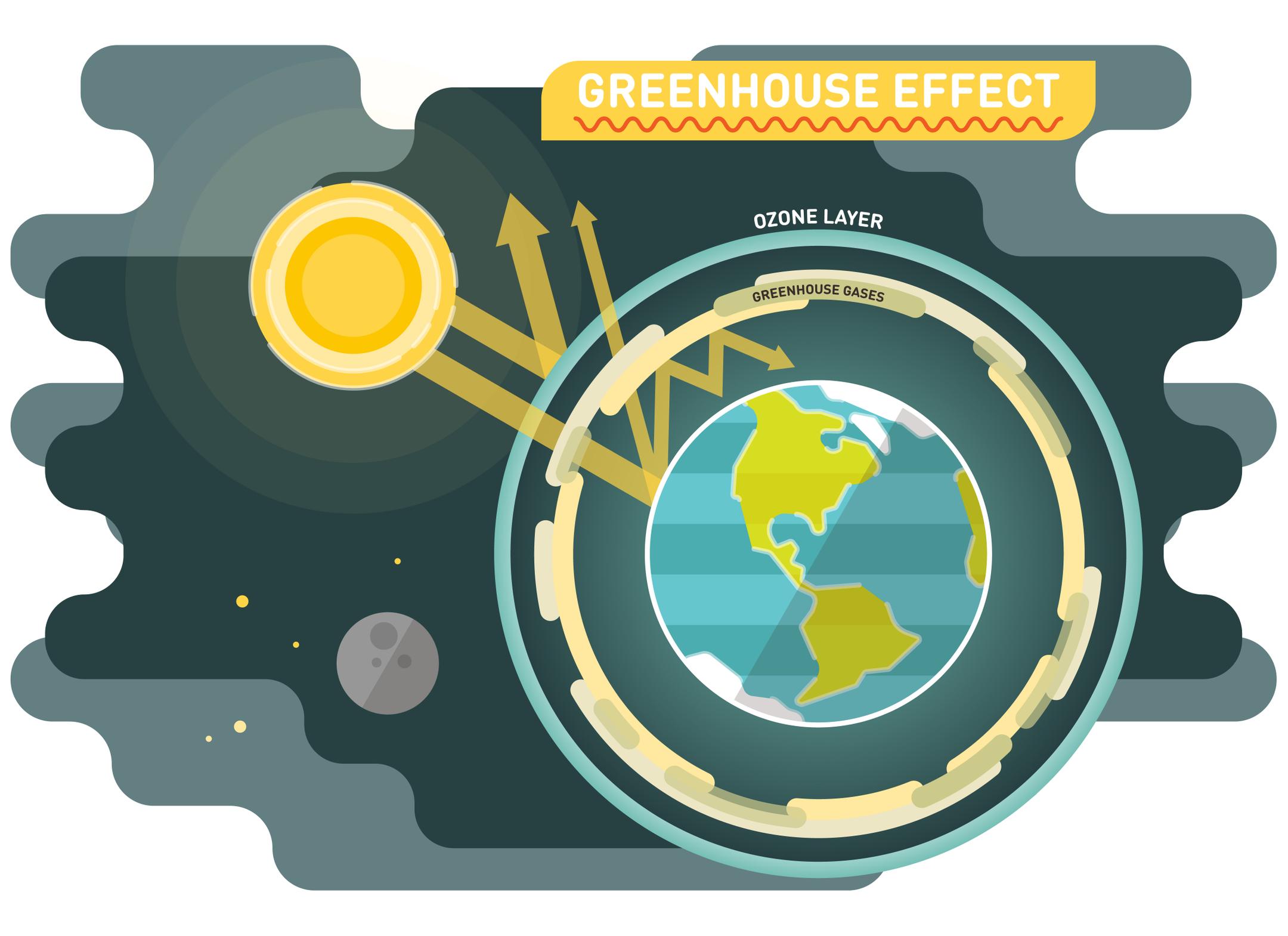
Altogether, this cycle of absorption and re-radiation by greenhouse gases impedes the loss of heat from our atmosphere to space, creating the greenhouse effect. Increases in the amount of greenhouses gases will mean that more heat is trapped, increasing the amount of energy in the Earth system (Earth’s energy budget), and raising Earth’s temperature. This increase in Earth’s average temperature is also known as global warming. Greenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them. The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere.
greenhouse effect
This paper presents an in-depth exploration of the current state of research on Magnetocaloric Effect (MCE) materials, examining various types of MCE materials and their respective potentials. The focus is particularly directed towards perovskite manganite materials due to their numerous advantages over other materials. Additionally, crucial parameters defining the MCE properties of perovskite manganite materials are discussed comprehensively, both at a fundamental level and in detail.
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. With the increase in population, the utilization of fossil fuels has increased.
For example, ISO is an International Standard for greenhouse gas accounting and verification. It provides organizations with a framework for measuring and reporting greenhouse gas emissions, as well as for verifying emission reductions and removals. This multi-part standard is an important tool to ensure transparency and uniformity across global efforts to combat climate change. To avoid unpredictable and uncontrollable changes in climate, humanity needs to act swiftly and in coordination, implementing comprehensive strategies to reduce carbon emissions, conserve biodiversity, and transition towards sustainable living globally. An important tool for informed action is to monitor Earth’s temperature and greenhouse gas emissions carefully. Reducing our greenhouse gas emissions will require significant effort at the international, national, and local levels.
Greenhouse effect and temperature
Global carbon emissions from fossil fuels reached record high in 2023 - Stanford University
Global carbon emissions from fossil fuels reached record high in 2023.
Posted: Tue, 05 Dec 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
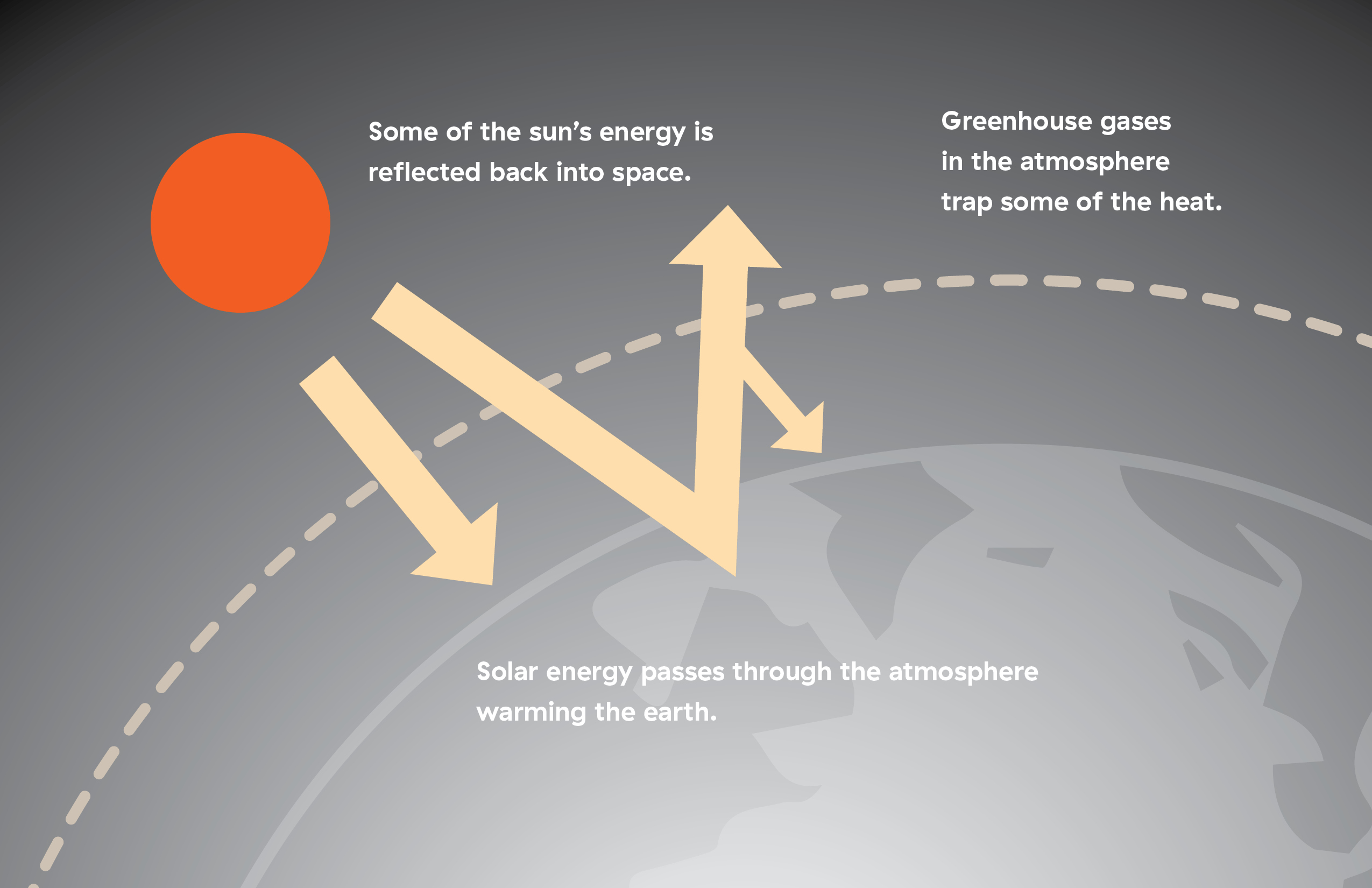
Greenhouse gas molecules release some of this thermal radiation back to Earth’s surface, contributing to the build-up of heat. A simple greenhouse effect diagram can be helpful to describe the greenhouse effect, and what greenhouse gases are doing to the Earth’s atmosphere. At night, when the earth cools down the heat is radiated back into the atmosphere. During this process, the heat is absorbed by the greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere.
‘It’s now or never’: UN climate report’s 4 urgent takeaways
Arrhenius first refers to this “hot-house theory” of the atmosphere—which would be known later as the greenhouse effect—in his work Worlds in the Making (1903). The greenhouse effect is also expected to warm the worlds of other star systems. Many astronomers speak of a narrow habitable zone around a star — the area where a planet would be at the perfect distance to maintain liquid water on its surface, between 0.95 and 1.4 times the Earth-sun distance. A thick atmosphere of molecular hydrogen, which is a potent greenhouse gas, could potentially give a world clement temperatures even if it were 15 times farther from the sun than Earth is. Billions of years ago, when the sun was cooler and dimmer, Venus may have had a temperate climate that could have allowed for liquid water oceans on its surface.
The exchange of incoming and outgoing radiation that warms the Earth is often referred to as the greenhouse effect because a greenhouse works in much the same way. Earth is constantly bombarded with enormous amounts of radiation, primarily from the sun. This solar radiation strikes the Earth's atmosphere in the form of visible light, plus ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR) and other types of radiation that are invisible to the human eye.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), methane accounted for more than 12 percent of human-generated greenhouse gas emissions in 2021. While methane can come from natural sources like wetlands, more than half of all global methane emissions come from human activities like natural gas production and livestock-based agriculture. Today, climate change is the term scientists use to describe the complex shifts, driven by greenhouse gas concentrations, that are now affecting our planet’s weather and climate systems. Climate change encompasses not only the rising average temperatures we refer to as global warming but also extreme weather events, shifting wildlife populations and and habitats, rising seas, and a range of other impacts. Even though only a tiny amount of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere are greenhouse gases, they have a huge effect on climate. Sometime during this century, the amount of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is expected to double.

No comments:
Post a Comment